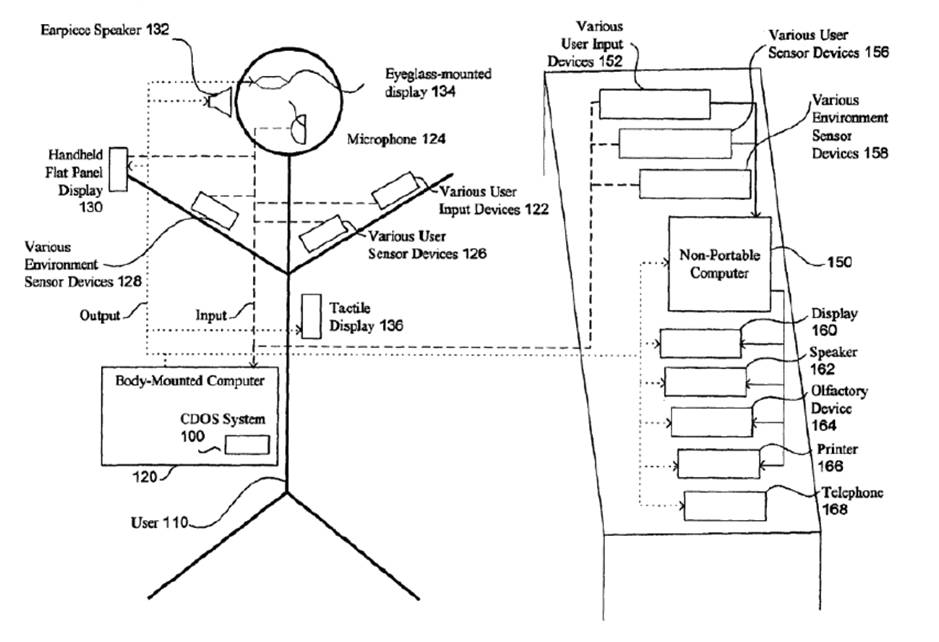
This is another fascinating 2005 patent assigned to Microsoft, helping manage the presentation of information based on user’s mental and physical state and cognitive load (and, yes, desired level of privacy).
U.S. Patent No. 6,874,127: Method and system for controlling presentation of information to a user based on the user’s condition.
- Assignee(s): Microsoft Corporation
- Inventor(s): Dan Newell, Kenneth H. Abbott
- Technology Category: Hybrid
- Issue Date: March 29, 2005
SharpBrains’ Take:
The ‘127 patent applies brain technology to information management with user models that consider cognitive load and mental state in order to determine how and what information is presented to the user. The specification discloses a number of technologies and approaches for determining physical and mental activity of the user, including EEG, EKG, heart rate and skin galvanometry sensors. While the specification, with nine illustration sheets and ten pages of written material, may raise question about the adequacy of support for the extensive claim set, the large number of claims (113), picket-fence formed by a number of broad independent claims (12) and significant rate of forward citations are among the factors making the ‘127 patent a key non-invasive neurotechnology patent.
Abstract:
A system for controlling presentation of information to a user based on the user’s current condition. In particular, the system monitors the user and the user’s environment, and creates and maintains an updated model of the current condition of the user. The user condition can include a variety of condition variables, including abstract concepts such as the user’s current cognitive load, desired level of privacy for output information, and desired scope of audience for output information. Upon receiving output information to be presented to the user (e.g., from an application program), the system determines an appropriate output device and an appropriate format with which to present the information to the user, and then presents the output information. The system can also receive description information about the output information that describes relevant factors for determining when and how to present the output information (e.g., the importance and urgency of the output information, the consequences of the user not receiving or ignoring the output information, etc.). Some versions of the system execute on a wearable computer having a variety of available output display devices.
Illustrative Claim 83. A method for presenting output information to a user of a computer, the computer able to output information to a first display device and a second display device, the first and second display devices having different display characteristics, the method comprising:
- selecting either the first display device or the second display device based on a predicted preference of the user, the predicted preference being a predicted mental state of the user indicating on which of the display devices the user would prefer to receive the output information, the selecting based at least in part on a mapping between the predicted mental state and the display devices that indicates which of the display devices are suitable for presenting information in accordance with various predicted mental states; and
- presenting the output information on the selected display device consistently with the predicted preference.
 To learn more about market data, trends and leading companies in the digital brain health space –digital platforms for brain/ cognitive assessment, monitoring and enhancement– check out this market report. To learn more about our analysis of 10,000+ patent filings, check out this IP & innovation neurotech report.
To learn more about market data, trends and leading companies in the digital brain health space –digital platforms for brain/ cognitive assessment, monitoring and enhancement– check out this market report. To learn more about our analysis of 10,000+ patent filings, check out this IP & innovation neurotech report.
The post Managing information flow based on user’s mental state and cognitive load: Key Neurotech Patent #19 appeared first on SharpBrains.